In 2023, Generative AI transformed the technological landscape, setting the stage for what many declared the “Year of Agents” in 2024. These autonomous, decision-making AI systems promised to revolutionize human-machine collaboration across industries. Yet as we navigate 2025, the proliferation of “Agentic AI” marketing has raised an important question: Are we witnessing genuine innovation or falling prey to “Agent Washing”?
This blog will explore the core principles of Agentic AI, distinguish it from automation and enhanced workflows, and outline actionable strategies for deploying true agents in industrial contexts.
What Is True Agentic AI?
A true agent isn’t just software that automates predefined tasks or interacts with large language models (LLMs) for deterministic workflows. Instead, it embodies human-like agency by reasoning, learning, and acting autonomously with purpose.
Arthur Kordon’s foundational principles for true Agentic AI provide a useful framework:
- Learning: The agent must acquire knowledge and improve over time, adapting to dynamic conditions.
- Prediction: It should anticipate outcomes, explore counterfactuals, and assess “what-if” scenarios.
- Reasoning and Decision-Making: The agent must apply logical reasoning to make context-aware decisions and act autonomously to achieve specific objectives.
Without these capabilities, what is marketed as an “agent” is often just a glorified assistant or workflow tool.
The Distinction: Automation, Workflows, and True Agents
Understanding the difference between automation, AI-enhanced workflows, and Agentic AI is critical for industrial decision-makers:
-
Traditional Automation:
- Executes predefined, rule-based tasks.
- Reliable for structured, repetitive processes.
- Lacks adaptability.
-
AI-Enhanced Workflows:
- Adds AI (often LLMs) to improve existing workflows.
- Enhances user experience and streamlines processes.
- Still follows deterministic paths.
-
True Industrial AI Agents:
- Operate autonomously, handling non-deterministic tasks.
- Learn from real-time data and adapt strategies like experienced operators.
- Collaborate with other systems to deliver complex, multi-faceted outcomes.
Example Use Case:
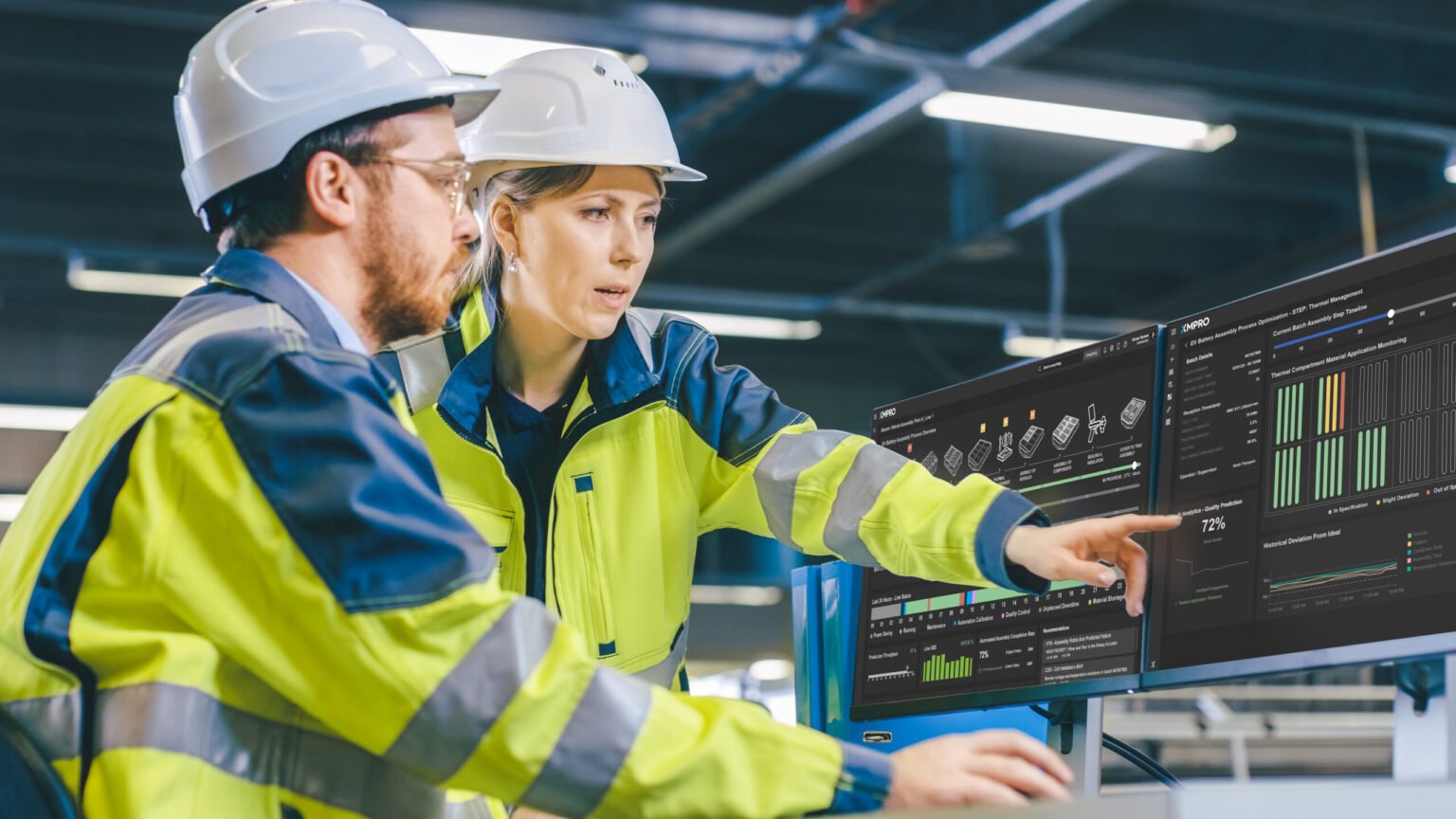
A manufacturing plant using traditional automation might schedule maintenance based on time intervals. An AI-enhanced workflow might predict failure based on historical patterns. A true agent, however, would analyze real-time sensor data, anticipate potential failures, and autonomously optimize maintenance schedules—coordinating with other agents to minimize downtime and costs.
Avoiding “Agent Washing”
The current market’s rush to brand tools as “agents” risks obscuring genuine progress. As Michael Carroll aptly described, many so-called agents are merely automation tools with shiny new labels. To identify true Agentic AI, ask:
- Does the system improve autonomously over time?
- Can it predict outcomes and explore alternative scenarios?
- Does it operate independently, beyond rigid rule sets or workflows?
- Can it collaborate effectively with other agents and systems?
- Does it provide unique, transformational value?
Agentic AI in Action: Industrial Use Cases
-
Predictive Maintenance in Mining:
Agents monitor equipment conditions, predict failures, and autonomously schedule maintenance—reducing downtime and improving safety. -
Production Optimization in Manufacturing:
Agents analyze data across supply chains, adjust production schedules in real-time, and minimize resource waste. -
Operational Resilience in Utilities:
Agents identify system anomalies, predict service interruptions, and deploy countermeasures, ensuring continuous operation.
The Path Forward: Embracing Agents with Caution
Industrial leaders must strike a balance between embracing innovation and avoiding overhyped solutions. The next 6–12 months will be pivotal in distinguishing genuine Agentic AI capabilities from exaggerated claims.
Key Recommendations:
- Start Small: Focus on targeted challenges where agents can provide measurable value.
- Design for Collaboration: Build agents that integrate seamlessly into existing workflows.
- Emphasize Learning: Choose systems that continuously improve through real-world use.
- Experiment and Learn: Use early implementations to refine processes and measure impact.
Conclusion: 2025—The Year of Transformation or Agent Washing?
The promise of Agentic AI lies in its ability to augment human expertise, adapt to complexity, and deliver outcomes that traditional systems cannot achieve. By cutting through the hype and focusing on measurable value, industrial organizations can harness this transformative technology to drive operational excellence.
Ready to explore how XMPro’s intelligent solutions can help your organization achieve its goals?
Learn more about XMPro’s AI capabilities and get started today.