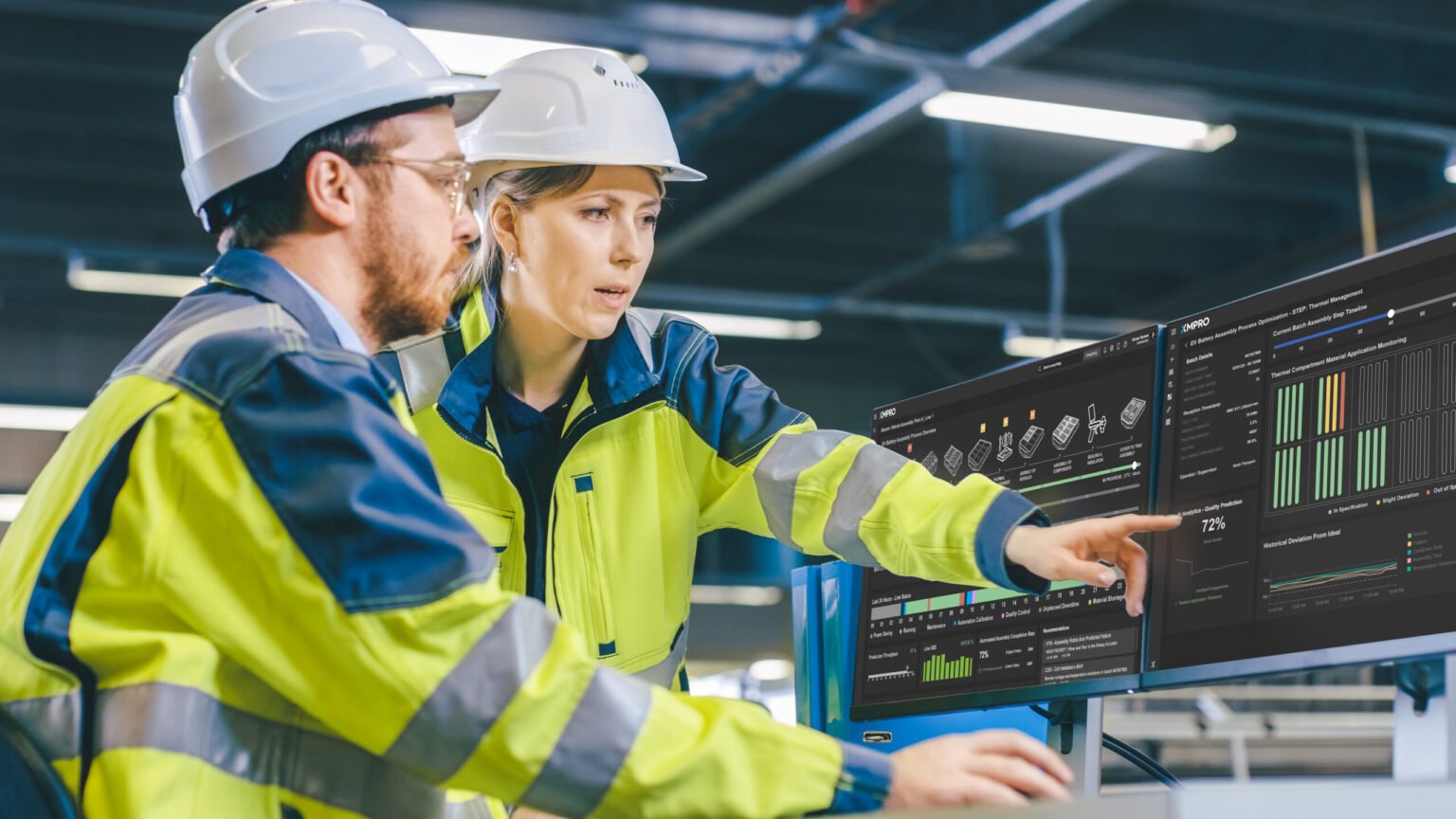
Edge computing is a distributed computing paradigm that brings computation and data storage closer to the edge of a network, where data is generated and used. The goal of edge computing is to reduce the amount of data that needs to be transmitted over the network, and to improve the speed and efficiency of data processing.
Digital twins can utilize edge computing in several ways. For example, a digital twin of a manufacturing plant could be implemented at the edge of the network, allowing it to process and analyze data from sensors and other devices in real-time, without the need to transmit the data to a centralized server for processing. This can help improve the responsiveness and accuracy of the digital twin, and allow it to make more informed decisions.
Edge computing can also be used to support the development and deployment of digital twins in resource-constrained or remote environments, where access to the cloud or other centralized resources may be limited. In these cases, the edge computing platform can provide the necessary computing and storage resources to support the digital twin, without the need for a dedicated server or other infrastructure.
Overall, edge computing can help digital twins operate more efficiently, respond more quickly to changing conditions, and provide more accurate and reliable insights and predictions.