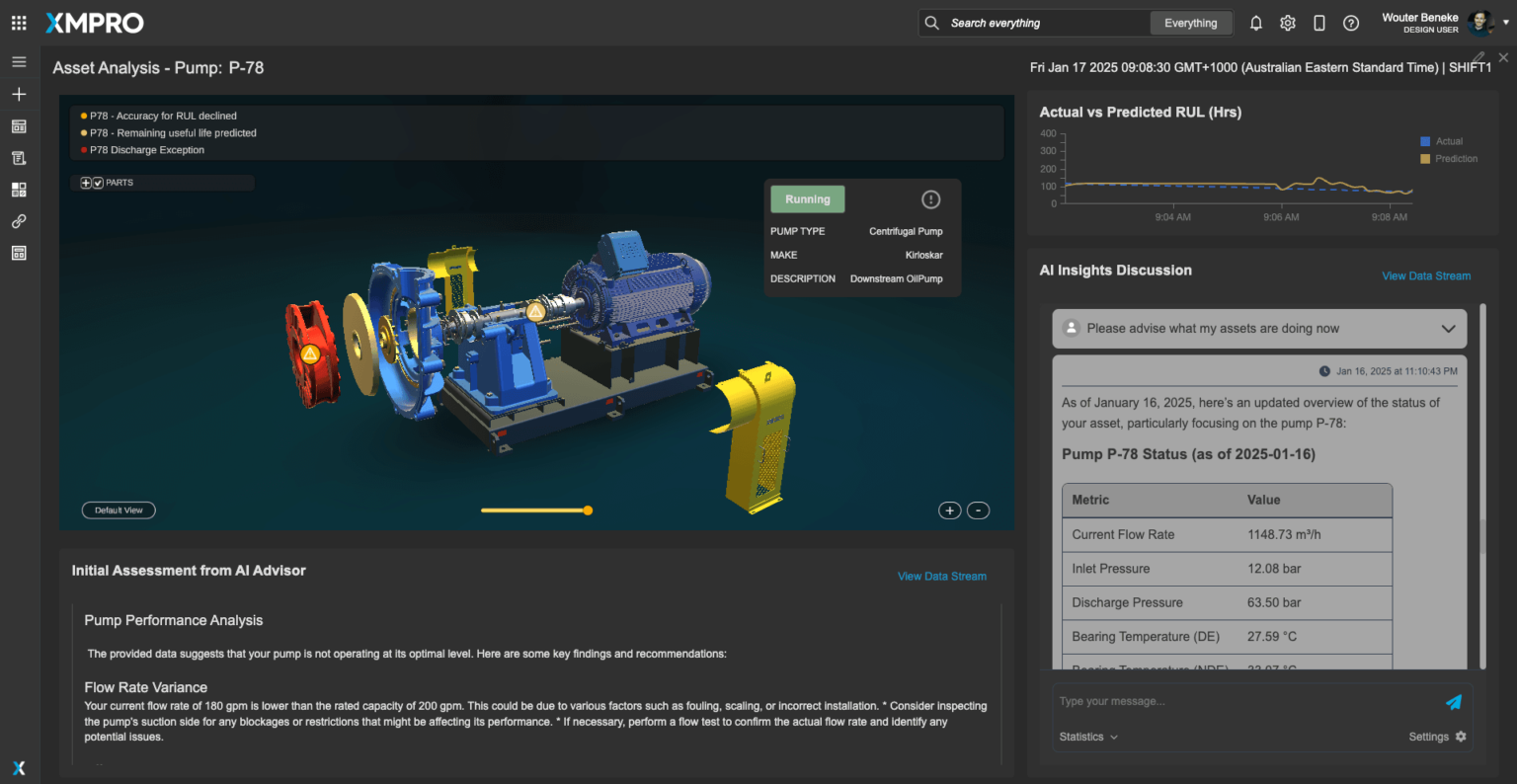
Introduction: Bridging the Gap Between AI Potential and Operational Reality
The promise of GenAI Virtual Assistants is undeniable: automation at scale, real-time decision-making, and personalized interactions that transform operations. Yet, for many industries, implementing these technologies comes with a host of challenges.
Accuracy concerns. Generic Large Language Models (LLMs) often produce plausible but incorrect responses, or “hallucinations.” In industries like manufacturing, healthcare, or logistics, these inaccuracies can lead to costly errors, operational inefficiencies, or even safety risks.
System integration hurdles. Many virtual assistants fail to integrate seamlessly with real-time data sources, legacy applications, or enterprise systems. Without this integration, assistants cannot deliver actionable, context-aware insights.
Governance gaps. Virtual assistants are being entrusted with critical operational decisions. Without clear governance frameworks, the risk of unsafe or non-compliant actions increases exponentially.
Scaling complexities. While building a proof-of-concept (PoC) assistant for a single use case is manageable, scaling it across multiple use cases, departments, or locations often results in bottlenecks in deployment, monitoring, and maintenance.
These pain points prevent organizations from fully realizing the transformative potential of GenAI Virtual Assistants. To address these challenges, enterprises need a structured approach grounded in verified data, robust governance, and scalable infrastructure.
Defining the Foundation for Reliable and Scalable Virtual Assistants
Reliability and scalability are fundamental to the success of any GenAI Virtual Assistant. Reliability ensures that the assistant delivers consistent, accurate, and actionable insights, even in complex or high-stakes scenarios.
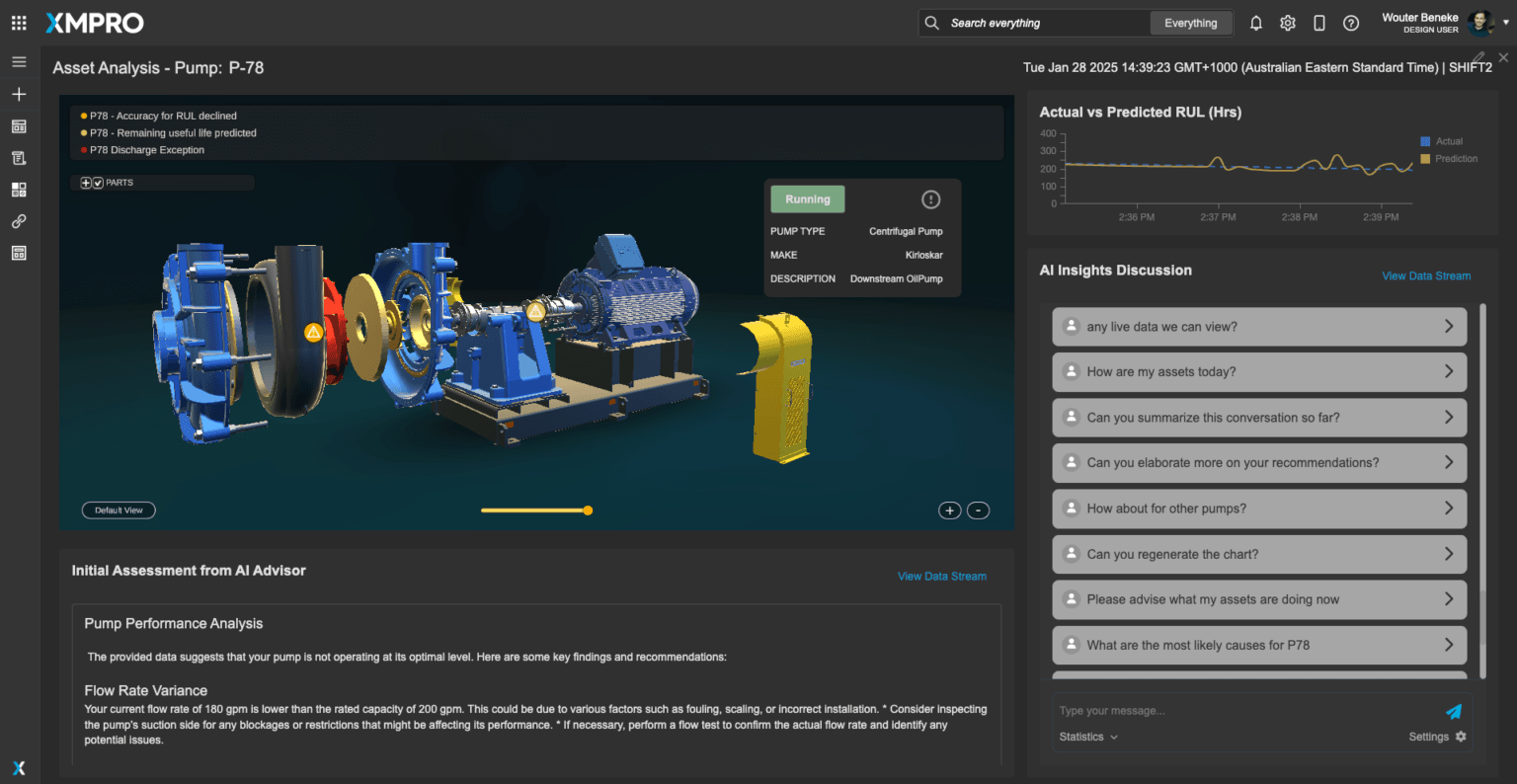
For example, in predictive maintenance, a reliable assistant must correctly interpret sensor data to alert operators about equipment risks before they escalate.
Scalability, on the other hand, involves expanding the assistant’s functionality to multiple use cases and geographies without degradation in performance. For instance, a virtual assistant that monitors industrial equipment should seamlessly adapt to new assets, facilities, and operational needs as an organization grows.
Achieving these outcomes requires a structured approach built on verified data, robust validation mechanisms, strong governance frameworks, and scalable infrastructure.
The Challenges of Reliability at Scale
Organizations implementing GenAI Virtual Assistants often encounter four key challenges.
The first is accuracy and hallucination. LLMs are powerful tools, but without proper grounding in verified data, they can generate outputs that appear plausible but are factually incorrect. This is particularly problematic in specialized domains, where a single error can have costly or even dangerous consequences.
The second challenge is system integration. Virtual assistants must interact with real-time data sources, IoT platforms, enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems, and legacy software. Achieving this level of seamless integration requires significant technical expertise and often becomes a bottleneck in scaling deployments.
Governance and safety form the third challenge. As virtual assistants take on more critical roles, ensuring they operate within defined boundaries becomes increasingly important. Without clear operational guardrails, the risk of errors, safety violations, or regulatory non-compliance grows exponentially.
Finally, scaling infrastructure is a significant hurdle. While building a single-use assistant is manageable, scaling across multiple locations, departments, or use cases introduces complexities in deployment, monitoring, and maintenance.
How XMPro Overcomes These Challenges
XMPro’s Intelligent Business Operations Suite (iBOS) provides a robust foundation for building reliable and scalable GenAI Virtual Assistants. By addressing the critical challenges of accuracy, governance, integration, and scalability, XMPro ensures these assistants are optimized for industrial and operational use cases.
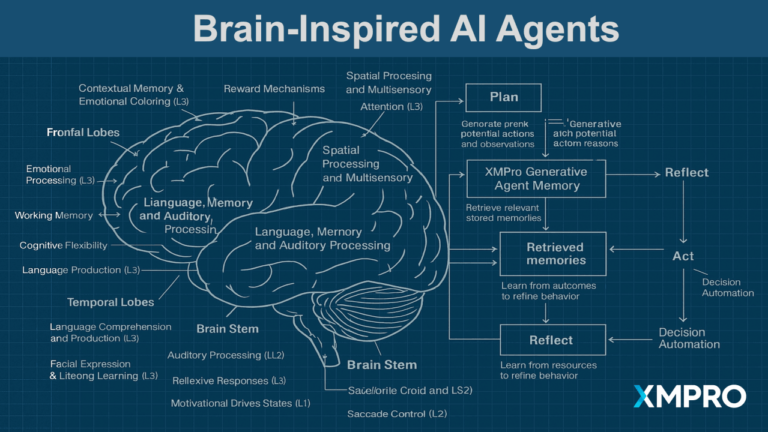
Ensuring Accuracy Through Knowledge Grounding
Accuracy is a key concern when deploying GenAI Virtual Assistants, particularly in environments where decisions have significant financial or safety implications. XMPro addresses this issue with Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG), which grounds the assistant’s outputs in verified, real-time data.
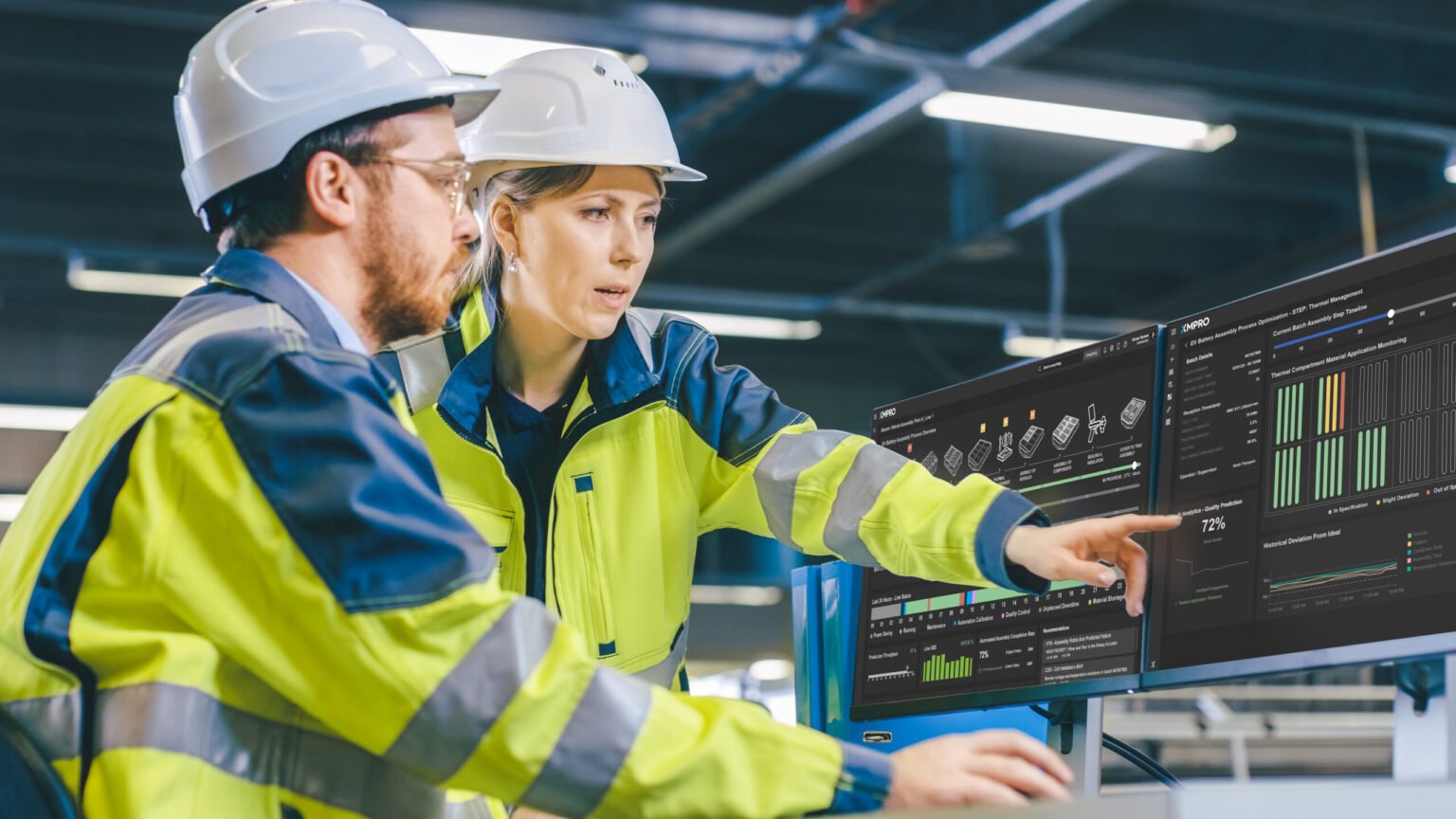
Instead of relying solely on the pre-trained knowledge of Large Language Models (LLMs), XMPro integrates data from live IoT sensors, operational logs, and engineering databases. For example, a virtual assistant used in predictive maintenance can access sensor data showing equipment temperature and vibration levels, cross-referencing this with historical trends and maintenance guidelines. This ensures that recommendations are accurate, relevant, and actionable.
Embedding AI Within Data Pipelines
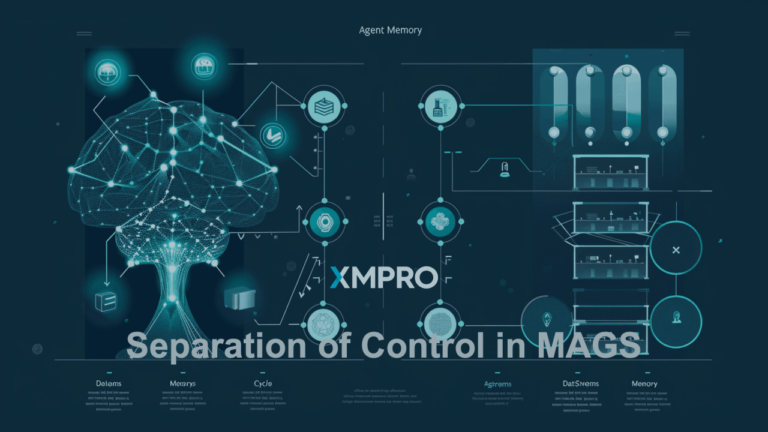
XMPro takes reliability and scalability a step further by embedding classical AI models directly within data pipelines. Classical AI models, purpose-built for tasks like anomaly detection, predictive maintenance, and optimization, handle the heavy lifting of analyzing raw data. This allows GenAI Virtual Assistants to focus on interpreting and communicating the results in a human-friendly manner.
For example, in a pipeline monitoring system, embedded classical AI models detect anomalies in pressure or flow rates. GenAI interprets these insights, explaining to operators why the anomaly occurred, its potential impact, and what actions should be taken. This division of labor ensures that each type of AI is used for what it does best—leaving computationally intensive analysis to classical AI and conversational interpretation to GenAI.
By integrating AI directly into data pipelines, XMPro creates a seamless flow of insights, where raw data is processed, analyzed, and contextualized before being presented by the virtual assistant. This approach enhances both accuracy and efficiency.
Governance Through Deontic Principles
XMPro ensures safety and compliance through a governance framework based on Deontic Principles. These principles clearly define what actions the assistant must take, what it can do under certain conditions, and what it must never do. For instance, a virtual assistant monitoring industrial equipment may be required to issue alerts when temperature thresholds are exceeded (obligations), may suggest shutting down equipment if further increases are detected (permissions), but is prohibited from directly shutting down operations without human approval (prohibitions).
This embedded governance ensures that GenAI Virtual Assistants operate safely and within organizational policies, providing trust and reliability in high-stakes environments.
Validation Layers for Enhanced Reliability
XMPro employs multiple layers of validation to ensure that outputs are reliable and actionable. This includes:
- Cross-validation processes, where insights are checked against predefined rules and real-time data.
- Confidence scoring, which evaluates the reliability of each output and triggers alerts for low-confidence recommendations.
- Integration with industrial-grade tools, ensuring all calculations and decisions are based on verified methodologies.
This validation process minimizes the risk of errors and ensures that virtual assistants deliver consistent, high-quality results.
Human Oversight for Critical Scenarios
Critical decision-making often requires a human touch, and XMPro ensures that humans remain in-the-loop for high-stakes scenarios. Virtual assistants provide recommendations but leave final decisions to operators or managers. For example, while an assistant may suggest shutting down a machine due to detected anomalies, the decision to act remains with a qualified engineer. This balance between automation and human judgment minimizes risks while improving efficiency.
Real-Time Contextual Awareness
XMPro connects virtual assistants to real-time operational data through its Data Streams functionality. This ensures that all recommendations and insights reflect the current state of operations rather than relying on outdated or static data. For instance, in a manufacturing plant, an assistant monitoring production efficiency can use live data on equipment performance and resource utilization to provide accurate, context-aware recommendations.
Scalability Through Modular Design
Scalability is built into XMPro’s architecture. Its modular design allows virtual assistants to be quickly adapted for new use cases, departments, or geographies without requiring extensive reengineering. Low-code tools simplify the creation and deployment of workflows, while automated testing and validation ensure consistency across implementations. This approach enables organizations to expand their virtual assistant capabilities as their operational needs grow.
Continuous Monitoring for Long-Term Performance
XMPro provides tools to continuously monitor the performance of virtual assistants, tracking metrics like response accuracy, system uptime, and user satisfaction. Any drop in performance can be quickly identified and addressed, ensuring the assistant remains reliable over time. This continuous feedback loop allows organizations to adapt their assistants to changing conditions, improving both short-term functionality and long-term scalability.
Step-by-Step: Building Reliable GenAI Virtual Assistants
Building reliable and scalable GenAI Virtual Assistants requires a structured process that ensures accuracy, contextual relevance, and seamless integration. XMPro’s tools and methodologies provide the foundation for developing assistants that deliver actionable insights and adapt to various operational needs.
Step 1: Define a High-Value Use Case
The first step in building a reliable virtual assistant is to clearly define the specific problem it will address. Start with a high-value use case, such as predictive maintenance, anomaly detection, or customer support.
For example, a predictive maintenance assistant could focus on identifying early signs of equipment wear using IoT sensor data. Starting with a targeted application ensures the assistant is purpose-built to solve a specific business problem, setting the stage for reliability. This approach also makes it easier to demonstrate value quickly and establish a scalable foundation for future use cases.
Step 2: Gather and Integrate Data with Embedded AI
Once the use case is defined, the next step is to connect the assistant to relevant data sources. XMPro simplifies this process through its extensive library of data connectors, enabling seamless integration with real-time IoT sensors, operational databases, and other enterprise systems.
This is where embedded AI within data pipelines becomes critical. Classical AI models are deployed to process and analyze raw data, such as detecting anomalies, forecasting trends, or performing predictive analytics. For example, a classical AI model might analyze vibration and temperature data from machinery to detect early signs of mechanical failure.
After the data is processed, GenAI interprets the results, providing human-friendly explanations and actionable recommendations. This division of labor allows classical AI to handle computationally intensive tasks, while GenAI focuses on contextual interpretation and communication, ensuring the assistant delivers accurate and meaningful insights.
Step 3: Build and Test Workflows
With the data integrated, the next step is to design workflows that dictate how the assistant processes data, interprets results, and communicates insights. XMPro’s low-code platform enables users to quickly create workflows tailored to the specific use case, significantly reducing development time.
Testing these workflows is essential to ensure the assistant performs reliably under various scenarios. XMPro’s simulation tools allow for rigorous testing, such as simulating different levels of equipment stress or varying environmental conditions. This ensures the assistant is prepared to handle real-world complexities.
Validation layers are also incorporated during this step to enhance reliability. For instance, confidence scoring can be used to evaluate the assistant’s outputs, flagging low-confidence recommendations for review. This ensures that only high-quality, actionable insights are delivered to end-users.
Step 4: Deploy Across Platforms with Embedded Intelligence
Deployment is where the assistant becomes operational. XMPro supports deployment across a variety of platforms, such as Microsoft Teams, Slack, custom dashboards, or even factory-floor systems. This flexibility ensures that the assistant meets users wherever they need it most, from the control room to remote monitoring setups.
The role of embedded AI within data pipelines becomes even more critical during deployment. Classical AI handles the heavy lifting of analyzing incoming data streams, ensuring the assistant operates efficiently even in high-demand environments. Meanwhile, GenAI focuses on interpreting and delivering insights, allowing the system to scale across different platforms and geographies with minimal reconfiguration.
Step 5: Monitor and Continuously Optimize
Building a reliable assistant is not a one-time achievement—it requires continuous monitoring and improvement. XMPro provides built-in tools to track key performance metrics such as response accuracy, uptime, user satisfaction, and task completion rates.
A feedback loop is essential for optimizing performance. End-user feedback, combined with operational data, provides valuable insights for refining workflows and enhancing the assistant’s outputs. For instance, if users consistently need more context in the assistant’s responses, the templates can be updated to improve clarity and usability.
Performance monitoring also allows teams to identify and resolve potential bottlenecks in embedded AI models or workflows. If a predictive model begins generating false positives, it can be recalibrated without disrupting the assistant’s broader functionality. This continuous optimization ensures the assistant remains reliable and effective as operational needs evolve.
Delivering Scalable, Reliable Assistants
By following these steps, organizations can build GenAI Virtual Assistants that are not only reliable but also scalable across multiple use cases and environments. Starting with a clear focus, integrating data with embedded AI, designing robust workflows, and continuously monitoring performance ensures that the assistant delivers consistent, actionable insights.
Whether optimizing manufacturing processes, monitoring industrial equipment, or enhancing customer interactions, XMPro equips businesses with the tools to build virtual assistants that transform operations and deliver long-term value.
Real-World Benefits of XMPro-Driven Assistants
XMPro-powered virtual assistants deliver significant benefits. They enhance operational efficiency by automating repetitive tasks, freeing up employees to focus on higher-value activities. Reliable insights, grounded in real-time data, improve decision-making across the board, from maintenance planning to customer service.
Scalability is another major advantage. XMPro’s modular architecture allows organizations to expand their assistants to new use cases and geographies quickly and cost-effectively. The built-in governance framework ensures safety and compliance, reducing risks in high-stakes operations.
These benefits translate into measurable business outcomes, including reduced downtime, increased productivity, and improved user satisfaction.
Conclusion: Building the Future of Reliable AI
Building reliable and scalable GenAI Virtual Assistants is no longer a distant goal but a practical reality with XMPro. By addressing the challenges of accuracy, integration, governance, and scalability, XMPro empowers organizations to unlock the full potential of virtual assistants.
Whether you’re starting with a single-use case or planning an enterprise-wide rollout, XMPro provides the tools and frameworks needed to succeed. With its focus on reliability, safety, and scalability, XMPro enables businesses to create assistants that meet today’s operational needs while remaining adaptable for the future.
Ready to transform your operations? Request a demo of XMPro today and discover how we can help you build the future of reliable AI.